You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
On this day:
- Thread starter Singlemalt
- Start date
lokie
Well-Known Member
The First Auto Race: Thanksgiving 1895
The greatest dangers in America’s first auto race were frostbite and exposure.

Originally scheduled for for the Fourth of July 1895. To accommodate the contestants race day was postponed until Thanksgiving Day, November 28.
The year was 1895 and automobiles were still a great novelty. The Chicago Times Herald, planned to exploit the growing interest in motoring by sponsoring a 54-mile race from downtown Chicago to Evanston, Illinois, and back. It would be open to all qualifying vehicles, foreign or domestic, powered by gas, electricity, or steam. The top prize would be $2,000 (the equivalent of over $50,000 today).
Only six cars made it to the starting line.
Average speed of 7 mph, foul weather and race ending crashes ensued.
The driver of the Macy Benz tried to close Duryea’s lengthening lead, but late in the afternoon, Macy’s driver ran into a sleigh that had overturned in the street. He was able to extricate the car and resume driving, but he soon ran into a horse-drawn hackney cab, which damaged the car’s steering. The driver managed to roll the car in-between the trolley car tracks and drive between the tracks to next checkpoint. Mechanics spent 80 minutes putting the Benz back in running order. But by 6:15, the darkening sky and cold winds were too discouraging. The Macy Benz vehicle dropped out of the race.
At 7:18 p.m., Frank Duryea crossed the finish line. He’d taken 10 hours and 23 minutes to travel 52.4 miles.
Almost two hours later, Mueller’s Benz came in sight, but now the referee was driving. In one hand, he held the steering tiller and, in the other, held up Mueller, who’d collapsed from the cold.
The first US automobile race was over.


 www.saturdayeveningpost.com
www.saturdayeveningpost.com
The greatest dangers in America’s first auto race were frostbite and exposure.

Originally scheduled for for the Fourth of July 1895. To accommodate the contestants race day was postponed until Thanksgiving Day, November 28.
The year was 1895 and automobiles were still a great novelty. The Chicago Times Herald, planned to exploit the growing interest in motoring by sponsoring a 54-mile race from downtown Chicago to Evanston, Illinois, and back. It would be open to all qualifying vehicles, foreign or domestic, powered by gas, electricity, or steam. The top prize would be $2,000 (the equivalent of over $50,000 today).
Only six cars made it to the starting line.
Average speed of 7 mph, foul weather and race ending crashes ensued.
The driver of the Macy Benz tried to close Duryea’s lengthening lead, but late in the afternoon, Macy’s driver ran into a sleigh that had overturned in the street. He was able to extricate the car and resume driving, but he soon ran into a horse-drawn hackney cab, which damaged the car’s steering. The driver managed to roll the car in-between the trolley car tracks and drive between the tracks to next checkpoint. Mechanics spent 80 minutes putting the Benz back in running order. But by 6:15, the darkening sky and cold winds were too discouraging. The Macy Benz vehicle dropped out of the race.
At 7:18 p.m., Frank Duryea crossed the finish line. He’d taken 10 hours and 23 minutes to travel 52.4 miles.
Almost two hours later, Mueller’s Benz came in sight, but now the referee was driving. In one hand, he held the steering tiller and, in the other, held up Mueller, who’d collapsed from the cold.
The first US automobile race was over.


The First Auto Race: Thanksgiving 1895 | The Saturday Evening Post
The greatest dangers in America’s first auto race were frostbite and exposure.
Last edited:
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
On November 29, 1947, despite strong Arab opposition, the United Nations votes for the partition of Palestine and the creation of an independent Jewish state.
The modern conflict between Jews and Arabs in Palestine dates back to the 1910s, when both groups laid claim to the British-controlled territory. The Jews were Zionists, recent emigrants from Europe and Russia who came to the ancient homeland of the Jews to establish a Jewish national state. The native Palestinian Arabs sought to stem Jewish immigration and set up a secular Palestinian state.
Beginning in 1929, Arabs and Jews openly fought in Palestine, and Britain attempted to limit Jewish immigration as a means of appeasing the Arabs. As a result of the Holocaust in Europe, many Jews illegally entered Palestine during World War II. Radical Jewish groups employed terrorism against British forces in Palestine, which they thought had betrayed the Zionist cause. At the end of World War II, in 1945, the United States took up the Zionist cause. Britain, unable to find a practical solution, referred the problem to the United Nations, which on November 29, 1947, voted to partition Palestine.
The Jews were to possess more than half of Palestine, though they made up less than half of Palestine’s population. The Palestinian Arabs, aided by volunteers from other countries, fought the Zionist forces, but the Jews secured full control of their U.N.-allocated share of Palestine and also some Arab territory. On May 14, 1948, Britain withdrew with the expiration of its mandate, and the State of Israel was proclaimed by Jewish Agency Chairman David Ben-Gurion. The next day, forces from Egypt, Transjordan (now known as Jordan), Syria, Lebanon and Iraq invaded.
The Israelis managed to fight off the Arabs and then seize key territories, such as Galilee, the Palestinian coast, and a strip of territory connecting the coastal region to the western section of Jerusalem. In 1949, U.N.-brokered cease-fires left the State of Israel in permanent control of those conquered areas. The departure of hundreds of thousands of Palestinian Arabs from Israel during the war left the country with a Jewish majority.
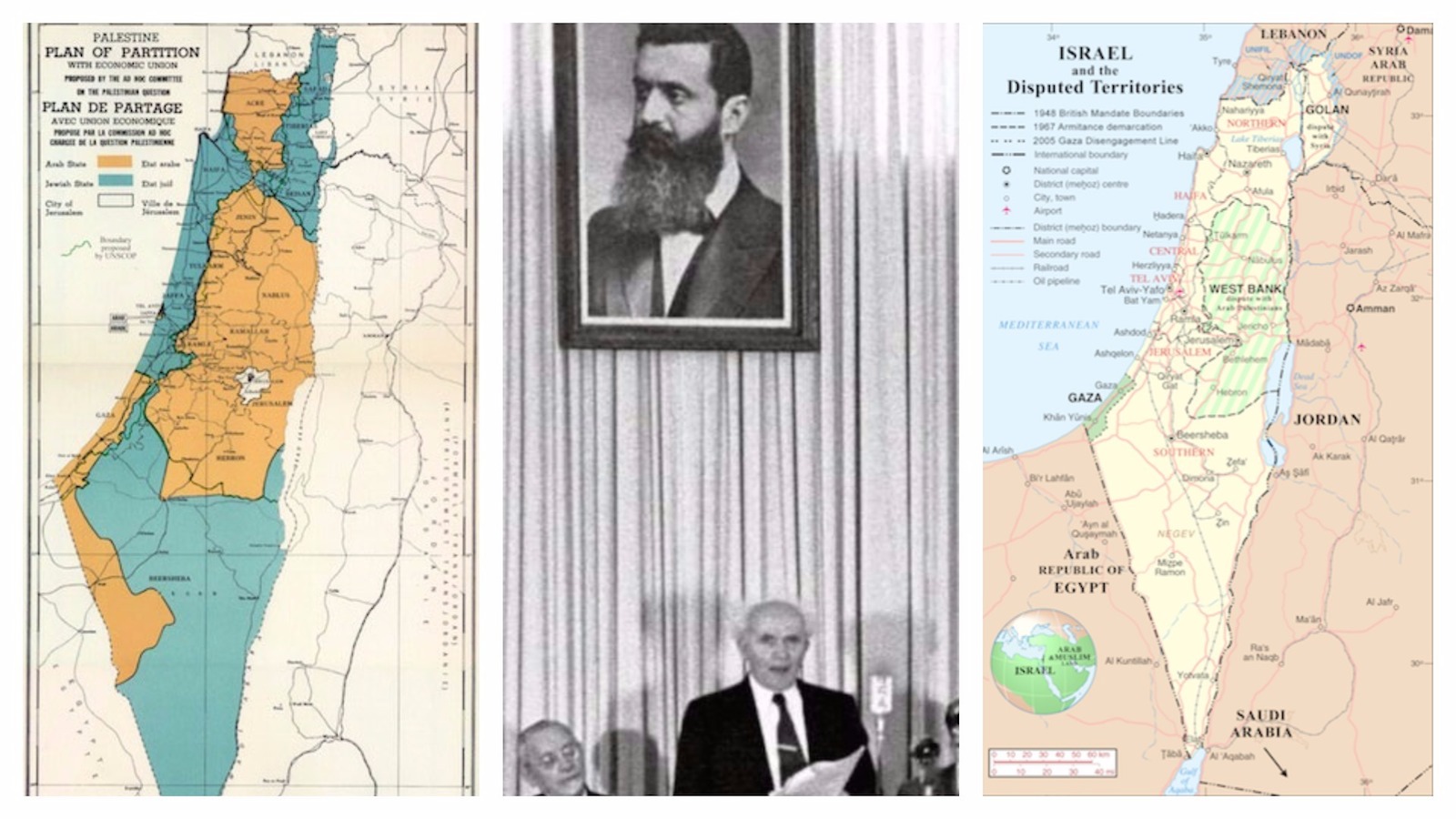
The United Nations Partition Plan of 1947 | My Jewish Learning
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 181

The Forgotten Miracle: Nov. 29, 1947
Last month saw the anniversary of one of the most significant events in Jewish history, perhaps the most significant since the Exodus from Egypt -- Nov. 29, 1947 -- the day the U.N. General Assembly voted 33-13 to partition Palestine into a Jewish state and an Arab state
 jewishjournal.com
jewishjournal.com
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
In Montgomery, Alabama on December 1, 1955, Rosa Parks is jailed for refusing to give up her seat on a public bus to a white man, a violation of the city’s racial segregation laws. The successful Montgomery Bus Boycott, organized by a young Baptist minister named Martin Luther King, Jr., followed Park’s historic act of civil disobedience.
“The mother of the civil rights movement,” as Rosa Parks is known, was born in Tuskegee, Alabama, in 1913. She worked as a seamstress and in 1943 joined the Montgomery chapter of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP).
According to a Montgomery city ordinance in 1955, African Americans were required to sit at the back of public buses and were also obligated to give up those seats to white riders if the front of the bus filled up. Parks was in the first row of the Black section when the white driver demanded that she give up her seat to a white man. Parks’ refusal was spontaneous but was not merely brought on by her tired feet, as is the popular legend. In fact, local civil rights leaders had been planning a challenge to Montgomery’s racist bus laws for several months, and Parks had been privy to this discussion.
Learning of Parks’ arrest, the NAACP and other African American activists immediately called for a bus boycott to be held by Black citizens on Monday, December 5. Word was spread by fliers, and activists formed the Montgomery Improvement Association to organize the protest. The first day of the bus boycott was a great success, and that night the 26-year-old Rev. Martin Luther King, Jr., told a large crowd gathered at a church, “The great glory of American democracy is the right to protest for right.” King emerged as the leader of the bus boycott and received numerous death threats from opponents of integration. At one point, his home was bombed, but he and his family escaped bodily harm.
The boycott stretched on for more than a year, and participants carpooled or walked miles to work and school when no other means were possible. As African Americans previously constituted 70 percent of the Montgomery bus ridership, the municipal transit system suffered gravely during the boycott. On November 13, 1956, the U.S. Supreme Court struck down Alabama state and Montgomery city bus segregation laws as being in violation of the equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. On December 20, King issued the following statement: “The year old protest against city buses is officially called off, and the Negro citizens of Montgomery are urged to return to the buses tomorrow morning on a non-segregated basis.” The boycott ended the next day. Rosa Parks was among the first to ride the newly desegregated buses.
Martin Luther King, Jr., and his nonviolent civil rights movement had won its first great victory. There would be many more to come.
Rosa Parks died on October 24, 2005. Three days later the U.S. Senate passed a resolution to honor Parks by allowing her body to lie in honor in the U.S. Capitol Rotunda.
Rosa Parks, In Her Own Words: A Short Documentary | Library of Congress Blog
The writings and social activism of civil rights icon Rosa Parks, as read and remembered by Bryan Stevenson, Condoleezza Rice, Ken Burns, Jacqueline Woodson, Sharon Robinson and others in this short documentary.
injinji
Well-Known Member
Actually there was another black lady who got arrested for not giving up her seat a few months earlier. But her being an unmarried woman in the family way, she was passed over for the iconic position. Not 100% Betsy Ross, but still a little spin involved.
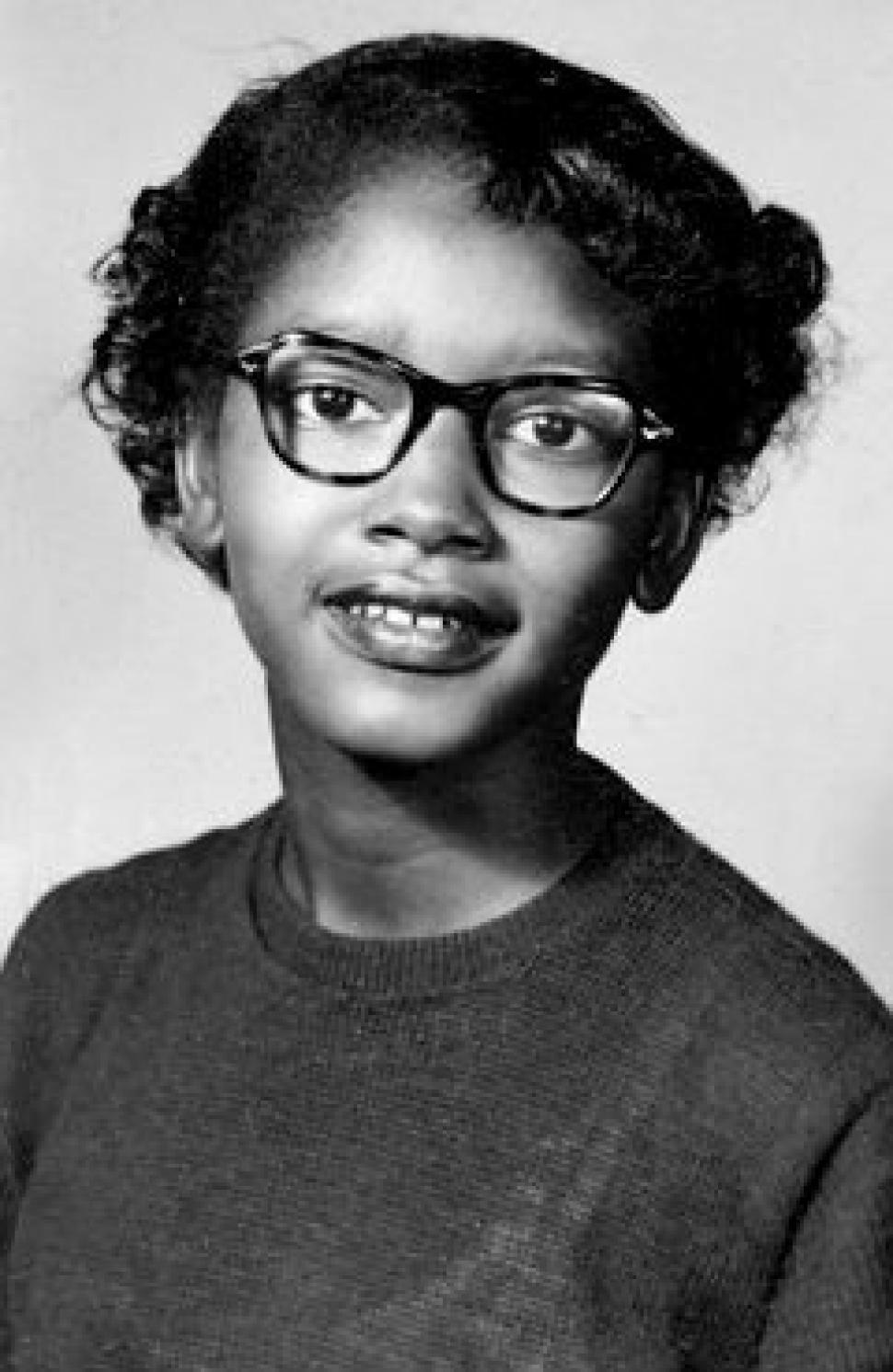

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org

Claudette Colvin - Wikipedia
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
Nice research, didn't know anything about Mrs. Colvin, who is still alive and trying to clear her nameActually there was another black lady who got arrested for not giving up her seat a few months earlier. But her being an unmarried woman in the family way, she was passed over for the iconic position. Not 100% Betsy Ross, but still a little spin involved.

Claudette Colvin - Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org

A Civil Rights Pioneer Seeks to Have Her Record Cleared (Published 2021)
Claudette Colvin refused to give up her bus seat to a white woman in Montgomery, Ala., in March 1955, nine months before Rosa Parks. Now 82, she says that justice from the court system is overdue.
injinji
Well-Known Member
I listen to too much NPR.Nice research, didn't know anything about Mrs. Colvin, who is still alive and trying to clear her name

A Civil Rights Pioneer Seeks to Have Her Record Cleared (Published 2021)
Claudette Colvin refused to give up her bus seat to a white woman in Montgomery, Ala., in March 1955, nine months before Rosa Parks. Now 82, she says that justice from the court system is overdue.www.nytimes.com
injinji
Well-Known Member
One of my favorite SNL skits was when no one could understand his lunch order, so he had to sing it.The Ozz man turned 73 today, this is what he had to say about it.
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
Early in the predawn hours of December 4, 1969, a Peoples Gas truck pulled up in front of an apartment building at 2337 W. Monroe St. in the West Side of Chicago. Fourteen plainclothes Chicago Police officers quietly filed out of the undercover truck, armed with pistols, a shotgun, a machine gun, and a detailed map of their target, an apartment occupied by leaders of the Chicago chapter of the Black Panther Party.
The map clearly identified the bedroom of Fred Hampton, the 21-year-old “chairman” of the Chicago Black Panthers, who was asleep beside his eight-month-pregnant fiancée. At 4:30 a.m., the police kicked down the front door and started shooting. Ballistics reports later showed that they fired more than 90 times, including machine gun rounds through exterior walls and windows.
When the volley of bullets finally stopped, four of the young Black Panthers inside the apartment lay shot and critically wounded, and two had been killed. The first was Mark Clark, who reached for his own shotgun before taking a bullet through the heart. The second was Fred Hampton, gunned down in his bed.
The police were acting under the orders of Edward Hanrahan, the Cook County state’s attorney, who held a press conference claiming that his officers were surprise-attacked by the Black Panthers as the police tried to execute a search warrant for illegal weapons in the apartment.
“The immediate, violent, criminal reaction of the occupants in shooting at announced police officers emphasizes the extreme viciousness of the Black Panther Party,” said Hanrahan.
While it didn’t take long for Hanrahan’s account to fall apart, it took more than a decade for the whole disturbing truth to come to light.
Not only was the killing of Hampton and Clark a cold-blooded assassination of two militant Black activists, but documents later revealed it was coordinated by the FBI as part of a secret program to neutralize and destroy the Black Panther Party, which FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover privately called “the greatest threat to the internal security of the country.”

The 1969 Raid That Killed Black Panther Leader Fred Hampton | HISTORY
Some details around the 1969 police shooting of Hampton and other Black Panther members took decades to come to light.
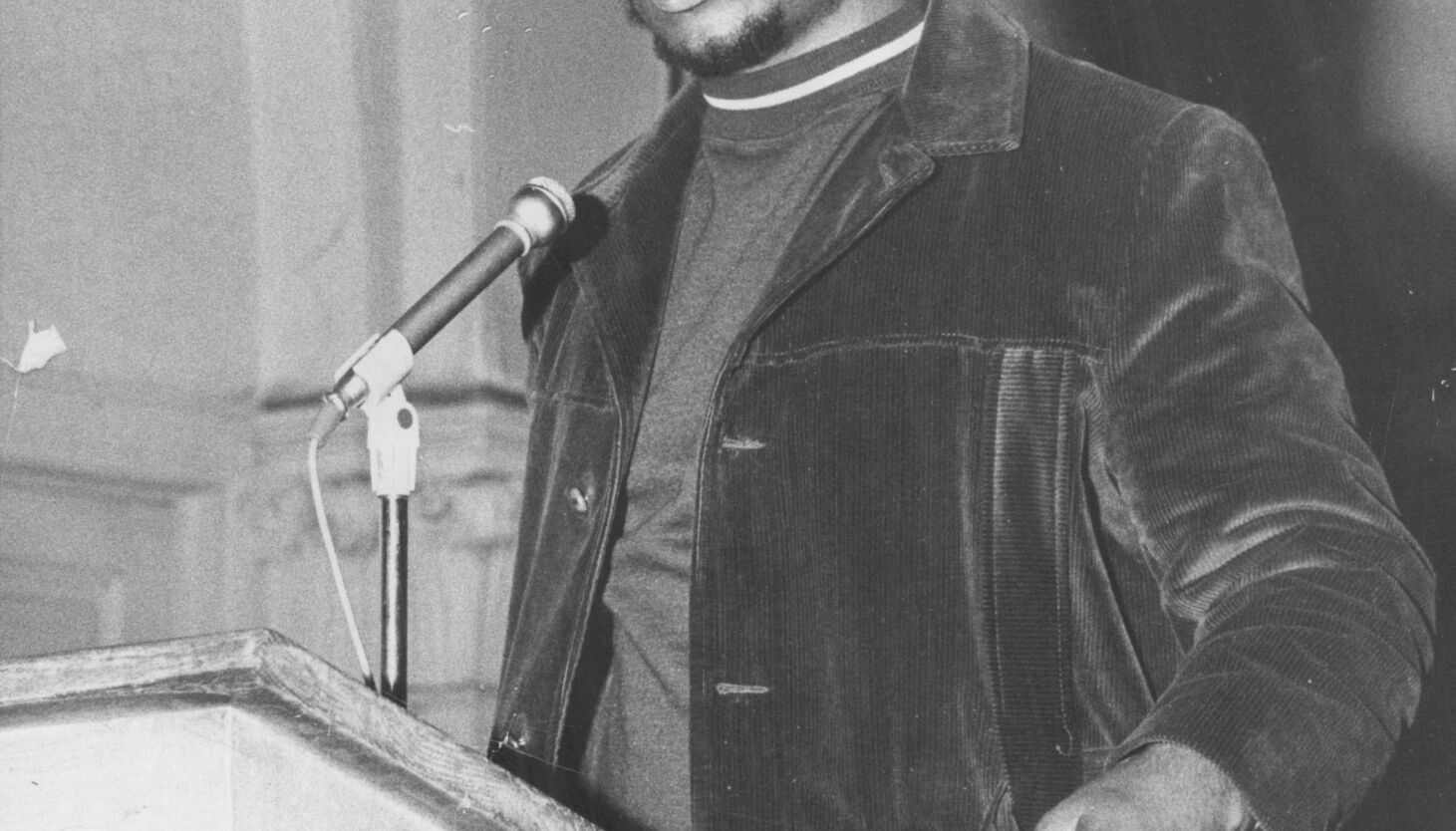

The killing of two Black Panthers, the secrets of the FBI — and our nation’s long fight for police reform
Newly released documents shed disturbing light on the FBI’s involvement in a 1969 police raid that resulted in the deaths of Fred Hampton and Mark Clark.

Black Panthers and Fred Hampton | People's Law Office
Fred Hampton and Mark Clark of the Illinois Chapter of the Black Panther Party were killed by Chicago police on December 4, 1969.
peopleslawoffice.com
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
1933 December 05: The 21st Amendment to the U.S. Constitution is ratified, repealing the 18th Amendment and bringing an end to the era of national prohibition of alcohol in America. At 5:32 p.m. EST, Utah became the 36th state to ratify the amendment, achieving the requisite three-fourths majority of states’ approval. Pennsylvania and Ohio had ratified it earlier in the day.
The movement for the prohibition of alcohol began in the early 19th century, when Americans concerned about the adverse effects of drinking began forming temperance societies. By the late 19th century, these groups had become a powerful political force, campaigning on the state level and calling for national liquor abstinence. Several states outlawed the manufacture or sale of alcohol within their own borders. In December 1917, the 18th Amendment, prohibiting the “manufacture, sale, or transportation of intoxicating liquors for beverage purposes,” was passed by Congress and sent to the states for ratification. On January 29, 1919, the 18th Amendment achieved the necessary three-fourths majority of state ratification. Prohibition essentially began in June of that year, but the amendment did not officially take effect until January 29, 1920.
In the meantime, Congress passed the Volstead Act on October 28, 1919, over President Woodrow Wilson’s veto. The Volstead Act provided for the enforcement of Prohibition, including the creation of a special Prohibition unit of the Treasury Department. In its first six months, the unit destroyed thousands of illicit stills run by bootleggers. However, federal agents and police did little more than slow the flow of booze, and organized crime flourished in America. Large-scale bootleggers like Al Capone of Chicago built criminal empires out of illegal distribution efforts, and federal and state governments lost billions in tax revenue. In most urban areas, the individual consumption of alcohol was largely tolerated and drinkers gathered at “speakeasies,” the Prohibition-era term for saloons.
Prohibition, failing fully to enforce sobriety and costing billions, rapidly lost popular support in the early 1930s. In 1933, the 21st Amendment to the Constitution was passed and ratified, ending national Prohibition. After the repeal of the 18th Amendment, some states continued Prohibition by maintaining statewide temperance laws. Mississippi, the last dry state in the Union, ended Prohibition in 1966..
lokie
Well-Known Member
December 5, 1848 – President Polk Catalyzes the California Gold Rush

On this day in history, President James K. Polk, in his State of the Union address, proclaimed:
The California Gold Rush was officialy acknowledged by the president of the United States.
Edit to add:


DESCRIPTION This small piece of yellow metal is believed to be the first piece of gold discovered in 1848 at Sutter's Mill in California, launching the gold rush.

 americanhistory.si.edu
americanhistory.si.edu

On this day in history, President James K. Polk, in his State of the Union address, proclaimed:
"It was known that mines of the precious metals existed to a considerable extent in California at the time of its acquisition [1848]. Recent discoveries render it probable that these mines are more extensive and valuable than was anticipated. The accounts of the abundance of gold in that territory are of such an extraordinary character as would scarcely command belief were they not corroborated by the authentic reports of officers in the public service who have visited the mineral district and derived the facts which they detail from personal observation.”
The California Gold Rush was officialy acknowledged by the president of the United States.
Edit to add:


DESCRIPTION This small piece of yellow metal is believed to be the first piece of gold discovered in 1848 at Sutter's Mill in California, launching the gold rush.
Gold Nugget
This small piece of yellow metal is believed to be the first piece of gold discovered in 1848 at Sutter's Mill in California, launching the gold rush.James…
Last edited:
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
The Halifax explosion of 1917 or the Great Halifax Explosion, on December 6, 1917, occurred when a munitions ship blew up in the harbour of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. Nearly 2,000 people died and some 9,000 were injured in the disaster, which flattened more than 1 square mile (2.5 square km) of the city of Halifax. The sudden and deafening fireball was the largest man-made explosion before nuclear weapons.
Shortly before 9:00 AM the Imo, a Norwegian steamship carrying supplies for the Belgian Relief Commission (a World War I-era relief organization), headed out of Halifax Harbour and found itself on a collision course with the French steamship Mont-Blanc. Unbeknownst to others in the harbour, the Mont-Blanc was carrying 2,925 metric tons (about 3,224 short tons) of explosives—including 62 metric tons (about 68 short tons) of guncotton, 246 metric tons (about 271 short tons) of benzol, 250 metric tons (about 276 short tons) of trinitrotoluene (TNT), and 2,367 metric tons (about 2,609 short tons) of picric acid—destined for the French war effort. After exchanging warning signals, both vessels initiated evasion maneuvers but ultimately collided.
The French ship caught fire after several drums of benzol—a highly combustible motor fuel derived from coke-oven gases—tipped over on the deck, spilling their contents, which ignited, and the vessel drifted into a pier. As crowds gathered, drawn in by the rising pall of smoke, emergency personnel tried to control the damage. However, just after 9:04 AM, the Mont-Blanc exploded. The blast and the resulting tsunami, which surged approximately 60 feet (18 metres) above the high-water mark, pressed some three blocks into the city. More than 1,600 buildings were destroyed by the wave, and debris was scattered for several miles. The force of the wave heaved the Imo toward the shore where it became grounded. In the aftermath of the explosion, hospitals were inundated with the wounded, and morgues struggled to identify and document the dead. News of the disaster spread quickly, and aid soon arrived from within Canada as well as from the United States.
The Halifax community remembers the disaster each December 6 with a service at the memorial bell tower located in Fort Needham Park. Internationally, the incident influenced the adoption of stricter maritime laws regarding cargo identification and harbour traffic control.
Halifax Explosion
Halifax was devastated on 6 December 1917 when two ships collided in the city's harbour, one of them a munitions ship loaded with explosives bound for the battl...
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
"Yesterday, December 7th, 1941—a date which will live in infamy—the United States of America was suddenly and deliberately attacked by naval and air forces of the Empire of Japan.
The United States was at peace with that nation and, at the solicitation of Japan, was still in conversation with its government and its emperor looking toward the maintenance of peace in the Pacific.
Indeed, one hour after Japanese air squadrons had commenced bombing in the American island of Oahu, the Japanese ambassador to the United States and his colleague delivered to our Secretary of State a formal reply to a recent American message. And while this reply stated that it seemed useless to continue the existing diplomatic negotiations, it contained no threat or hint of war or of armed attack.
It will be recorded that the distance of Hawaii from Japan makes it obvious that the attack was deliberately planned many days or even weeks ago. During the intervening time, the Japanese government has deliberately sought to deceive the United States by false statements and expressions of hope for continued peace.
The attack yesterday on the Hawaiian islands has caused severe damage to American naval and military forces. I regret to tell you that very many American lives have been lost. In addition, American ships have been reported torpedoed on the high seas between San Francisco and Honolulu.
Yesterday, the Japanese government also launched an attack against Malaya. Last night, Japanese forces attacked Hong Kong. Last night, Japanese forces attacked Guam. Last night, Japanese forces attacked the Philippine Islands. Last night, the Japanese attacked Wake Island. And this morning, the Japanese attacked Midway Island.
Japan has, therefore, undertaken a surprise offensive extending throughout the Pacific area. The facts of yesterday and today speak for themselves. The people of the United States have already formed their opinions and well understand the implications to the very life and safety of our nation.
As Commander in Chief of the Army and Navy, I have directed that all measures be taken for our defense. But always will our whole nation remember the character of the onslaught against us.
No matter how long it may take us to overcome this premeditated invasion, the American people in their righteous might will win through to absolute victory.
I believe that I interpret the will of the Congress and of the people when I assert that we will not only defend ourselves to the uttermost, but will make it very certain that this form of treachery shall never again endanger us.
Hostilities exist. There is no blinking at the fact that our people, our territory, and our interests are in grave danger.
With confidence in our armed forces, with the unbounding determination of our people, we will gain the inevitable triumph—so help us God.
I ask that the Congress declare that since the unprovoked and dastardly attack by Japan on Sunday, December 7th, 1941, a state of war has existed between the United States and the Japanese empire.”
-Franklin Roosevelt, Address to Congress, December 8, 1941

Eighty Years of Lies: President Franklin Roosevelt Told Public Pearl Harbor Was A Surprise Attack—However There Is Considerable Evidence Demonstrating Government Foreknowledge - CovertAction Magazine
“The war that we have carefully for yearsprovokedCatches us unprepared, amazed and indignant.Our warships are shotLike sitting ducks and […]
 covertactionmagazine.com
covertactionmagazine.com
Last edited:
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
John Lennon, a former member of the Beatles, the rock group that transformed popular music in the 1960s, is shot and killed by an obsessed fan in New York City, December 8, 1980.
The 40-year-old artist was entering his luxury Manhattan apartment building when Mark David Chapman shot him four times at close range with a .38-caliber revolver. Lennon, bleeding profusely, was rushed to the hospital but died en route. Chapman had received an autograph from Lennon earlier in the day and voluntarily remained at the scene of the shooting until he was arrested by police. For a week, hundreds of bereaved fans kept a vigil outside the Dakota–Lennon’s apartment building–and demonstrations of mourning were held around the world.
John Lennon was one half of the singing-songwriting team that made the Beatles the most popular musical group of the 20th century. The other band leader was Paul McCartney, but the rest of the quartet–George Harrison and Ringo Starr–sometimes penned and sang their own songs as well. Hailing from Liverpool, England, and influenced by early American rock and roll, the Beatles took Britain by storm in 1963 with the single “Please Please Me.” “Beatlemania” spread to the United States in 1964 with the release of “I Want to Hold Your Hand,” followed by a sensational U.S. tour. With youth poised to break away from the culturally rigid landscape of the 1950s, the “Fab Four,” with their exuberant music and good-natured rebellion, were the perfect catalyst for the shift.
The Beatles sold millions of records and starred in hit movies such as A Hard Day’s Night (1964). Their live performances were near riots, with teenage girls screaming and fainting as their boyfriends nodded along to the catchy pop songs. In 1966, the Beatles gave up touring to concentrate on their innovative studio recordings, such as 1967’s Sgt. Pepper’s Lonely Heart’s Club Band, a psychedelic concept album that is regarded as a masterpiece of popular music. The Beatles’ music remained relevant to youth throughout the great cultural shifts of the 1960s, and critics of all ages acknowledged the songwriting genius of the Lennon-McCartney team.
Lennon was considered the intellectual Beatle and certainly was the most outspoken of the four. He caused a major controversy in 1966 when he declared that the Beatles were “more popular than Jesus,” prompting mass burnings of Beatles’ records in the American Bible Belt. He later became an anti-war activist and flirted with communism in the lyrics of solo hits like “Imagine,” recorded after the Beatles disbanded in 1970. In 1975, Lennon dropped out of the music business to spend more time with his Japanese-born wife, Yoko Ono, and their son, Sean. In 1980, he made a comeback with Double-Fantasy, a critically acclaimed album that celebrated his love for Yoko and featured songs written by her.
On December 8, 1980, their peaceful domestic life on New York’s Upper West Side was shattered by 25-year-old Mark David Chapman. Psychiatrists deemed Chapman a borderline psychotic. He was instructed to plead insanity, but instead he pleaded guilty to murder. He was sentenced to 20 years to life. In 2000, New York State prison officials denied Chapman a parole hearing, telling him that his “vicious and violent act was apparently fueled by your need to be acknowledged.” He remains behind bars.
John Lennon is memorialized in “Strawberry Fields,” a section of Central Park across the street from the Dakota that Yoko Ono landscaped in honor of her husband.
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
On December 9, 1979, a commission of scientists declare that smallpox has been eradicated. The disease, which carries around a 30 percent chance of death for those who contract it, is the only infectious disease afflicting humans that has officially been eradicated.
Something similar to smallpox had ravaged humanity for thousands of years, with the earliest known description appearing in Indian accounts from the 2 Century BCE. It was believed that the Egyptian Pharaoh Ramses V died of smallpox in 1145 BCE; however, recent research indicates that the actual smallpox virus may have evolved as late as 1580 CE. A type of inoculation—introducing a small amount of the disease in order to bring on a mild case that results in immunity—was widespread in China by the 16th century.
There is no record of a smallpox-like illness in the Americas before European contact, and the fact that Europeans brought pox with them was a major factor in their conquest and near-eradication of many of the indigenous peoples of North, South and Central America. Smallpox was the leading cause of death in 18th century Europe, leading to many experiments with inoculation. In 1796 the English scientist Edward Jenner discovered a vaccine. Unlike other types of inoculation, Jenner’s vaccine, made from a closely-related disease that affects cows, carried zero risk of transmission.
Many European countries and American states made the vaccination of infants mandatory, and incidents of smallpox declined over the 19th and early 20th centuries. Compared to other epidemic diseases, such as polio or malaria, smallpox eradication was relatively simple because the disease lives only in humans, making human vaccination highly effective at stopping its spread, and its symptoms appear quickly, making it easy to identify and isolate outbreaks.
Starting in 1967, the World Health Organization undertook a worldwide effort to identify and stamp out the last remaining outbreaks of the disease. By the mid-70s, smallpox was only present in the Horn of Africa and parts of the Indian subcontinent. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in Somalia in 1977. Two years later, doctors proclaimed its eradication. The elimination of smallpox is one of the major successes in the history of science and medicine.
Almost two centuries after Jenner hoped that vaccination could annihilate smallpox, the 33rd World Health Assembly declared the world free of this disease on May 8, 1980. Many people consider smallpox eradication to be the biggest achievement in international public health.
Following the eradication of smallpox, scientists and public health officials determined there was still a need to perform research using the variola virus. They agreed to reduce the number of laboratories holding stocks of variola virus to only four locations. In 1981, the four countries that either served as a WHO collaborating center or were actively working with variola virus were the United States, England, Russia, and South Africa. By 1984, England and South Africa had either destroyed their stocks or transferred them to other approved labs. There are now only two locations that officially store and handle variola virus under WHO supervision: the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia, and the State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology (VECTOR Institute) in Koltsovo, Russia.
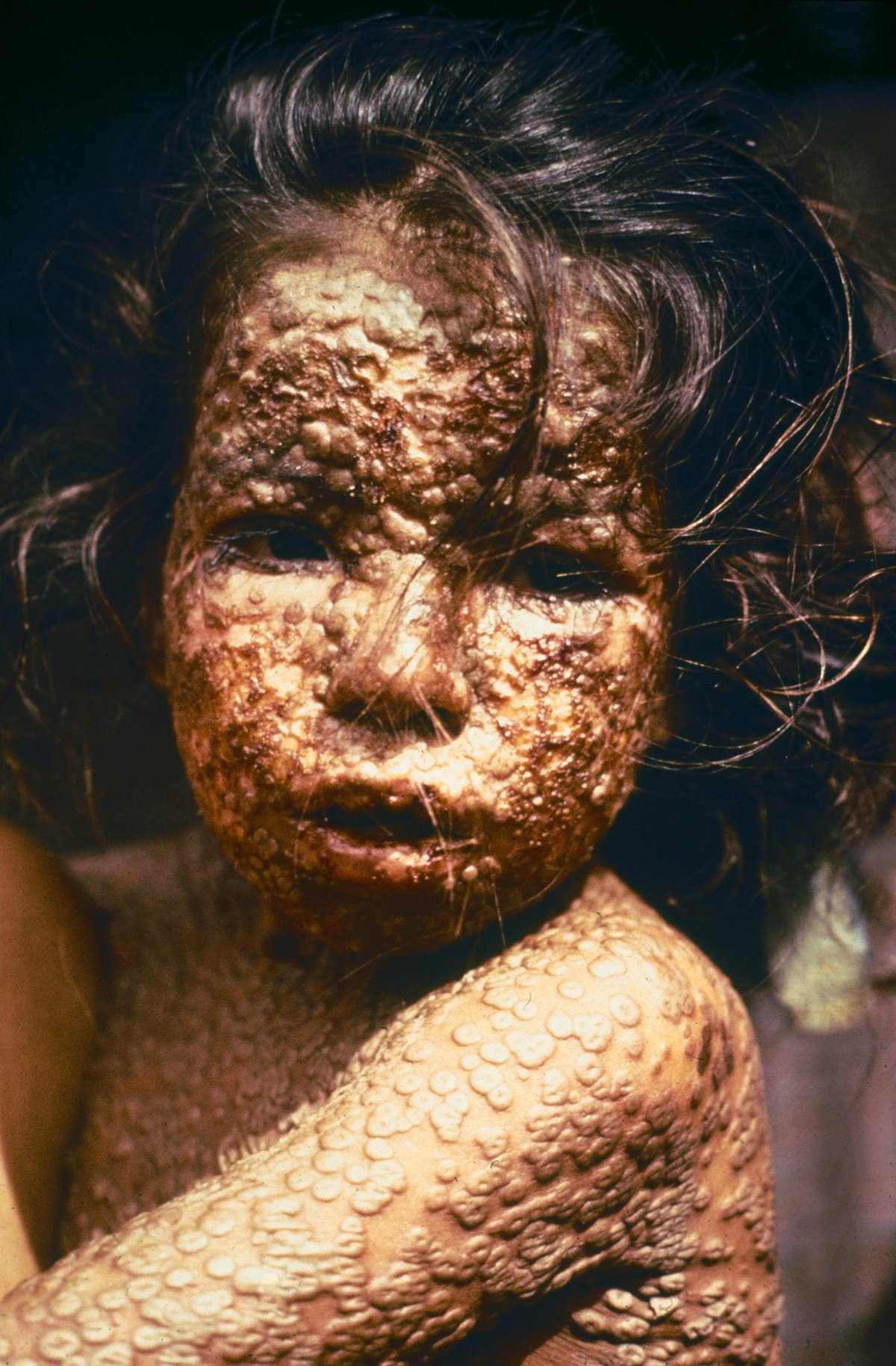

Smallpox - Wikipedia
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
On December 13, 1937, the Japanese Imperial Army marched into China's capital city of Nanking and proceeded to murder 300,000 out of 600,000 civilians and soldiers in the city. The six weeks of carnage would become known as the Rape of Nanking and represented the single worst atrocity during the World War II era in either the European or Pacific theaters of war.
The actual military invasion of Nanking was preceded by a tough battle at Shanghai that began in the summer of 1937. Chinese forces there put up surprisingly stiff resistance against the Japanese Army which had expected an easy victory in China. The Japanese had even bragged they would conquer all of China in just three months. The stubborn resistance by the Chinese troops upset that timetable, with the battle dragging on through the summer into late fall. This infuriated the Japanese and whetted their appetite for the revenge that was to follow at Nanking.
After finally defeating the Chinese at Shanghai in November, 50,000 Japanese soldiers then marched on toward Nanking. Unlike the troops at Shanghai, Chinese soldiers at Nanking were poorly led and loosely organized. Although they greatly outnumbered the Japanese and had plenty of ammunition, they withered under the ferocity of the Japanese attack, then engaged in a chaotic retreat. After just four days of fighting, Japanese troops smashed into the city on December 13, 1937, with orders issued to "kill all captives."
Their first concern was to eliminate any threat from the 90,000 Chinese soldiers who surrendered. To the Japanese, surrender was an unthinkable act of cowardice and the ultimate violation of the rigid code of military honor drilled into them from childhood onward. Thus they looked upon Chinese POWs with utter contempt, viewing them as less than human, unworthy of life.
The elimination of the Chinese POWs began after they were transported by trucks to remote locations on the outskirts of Nanking. As soon as they were assembled, the savagery began, with young Japanese soldiers encouraged by their superiors to inflict maximum pain and suffering upon individual POWs as a way of toughening themselves up for future battles, and also to eradicate any civilized notions of mercy. Filmed footage and still photographs taken by the Japanese themselves document the brutality. Smiling soldiers can be seen conducting bayonet practice on live prisoners, decapitating them and displaying severed heads as souvenirs, and proudly standing among mutilated corpses. Some of the Chinese POWs were simply mowed down by machine-gun fire while others were tied-up, soaked with gasoline and burned alive.
After the destruction of the POWs, the soldiers turned their attention to the women of Nanking and an outright animalistic hunt ensued. Old women over the age of 70 as well as little girls under the age of 8 were dragged off to be sexually abused. More than 20,000 females (with some estimates as high as 80,000) were gang-raped by Japanese soldiers, then stabbed to death with bayonets or shot so they could never bear witness.
Pregnant women were not spared. In several instances, they were raped, then had their bellies slit open and the fetuses torn out. Sometimes, after storming into a house and encountering a whole family, the Japanese forced Chinese men to rape their own daughters, sons to rape their mothers, and brothers their sisters, while the rest of the family was made to watch.
Throughout the city of Nanking, random acts of murder occurred as soldiers frequently fired their rifles into panicked crowds of civilians, killing indiscriminately. Other soldiers killed shopkeepers, looted their stores, then set the buildings on fire after locking people of all ages inside. They took pleasure in the extraordinary suffering that ensued as the people desperately tried to escape the flames by climbing onto rooftops or leaping down onto the street.
The incredible carnage - citywide burnings, stabbings, drownings, strangulations, rapes, thefts, and massive property destruction - continued unabated for about six weeks, from mid-December 1937 through the beginning of February 1938. Young or old, male or female, anyone could be shot on a whim by any Japanese soldier for any reason. Corpses could be seen everywhere throughout the city. The streets of Nanking were said to literally have run red with blood.
Those who were not killed on the spot were taken to the outskirts of the city and forced to dig their own graves, large rectangular pits that would be filled with decapitated corpses resulting from killing contests the Japanese held among themselves. Other times, the Japanese forced the Chinese to bury each other alive in the dirt.
After this period of unprecedented violence, the Japanese eased off somewhat and settled in for the duration of the war. To pacify the population during the long occupation, highly addictive narcotics, including opium and heroin, were distributed by Japanese soldiers to the people of Nanking, regardless of age. An estimated 50,000 persons became addicted to heroin while many others lost themselves in the city's opium dens.
In addition, the notorious Comfort Women system was introduced which forced young Chinese women to become slave-prostitutes, existing solely for the sexual pleasure of Japanese soldiers.
News reports of the happenings in Nanking appeared in the official Japanese press and also in the West, as page-one reports in newspapers such as the New York Times. Japanese news reports reflected the militaristic mood of the country in which any victory by the Imperial Army resulting in further expansion of the Japanese empire was celebrated. Eyewitness reports by Japanese military correspondents concerning the sufferings of the people of Nanking also appeared. They reflected a mentality in which the brutal dominance of subjugated or so-called inferior peoples was considered just. Incredibly, one paper, the Japan Advertiser, actually published a running count of the heads severed by two officers involved in a decapitation contest, as if it was some kind of a sporting match.
In the United States, reports published in the New York Times, Reader's Digest and Time Magazine, were greeted with skepticism from the American public. The stories smuggled out of Nanking seemed almost too fantastic to be believed.
Overall, most Americans had only a passing knowledge or little interest in Asia. Political leaders in both America and Britain remained overwhelmingly focused on the situation in Europe where Adolf Hitler was rapidly re-arming Germany while at the same time expanding the borders of the Nazi Reich through devious political maneuvers.
Back in Nanking, however, all was not lost. An extraordinary group of about 20 Americans and Europeans remaining in the city, composed of missionaries, doctors and businessmen, took it upon themselves to establish an International Safety Zone. Using Red Cross flags, they brazenly declared a 2.5 square-mile area in the middle of the city off limits to the Japanese. On numerous occasions, they also risked their lives by personally intervening to prevent the execution of Chinese men or the rape of women and young girls.
These Westerners became the unsung heroes of Nanking, working day and night to the point of exhaustion to aid the Chinese. They also wrote down their impressions of the daily scenes they witnessed, with one describing Nanking as "hell on earth." Another wrote of the Japanese soldiers: "I did not imagine that such cruel people existed in the modern world." About 300,000 Chinese civilians took refuge inside their Safety Zone. Almost all of the people who did not make it into the Zone during the Rape of Nanking ultimately perished.

Exposing The Rape Of Nanking
THE CHRONICLE OF humankind's cruelty is a long and sorry tale. But if it is true that even in such horror tales there are degrees of ruthlessness, then few atrocities can compare in intensity and scale to the rape of Nanking during World War II.
World Perceptions on the Rape of Nanking
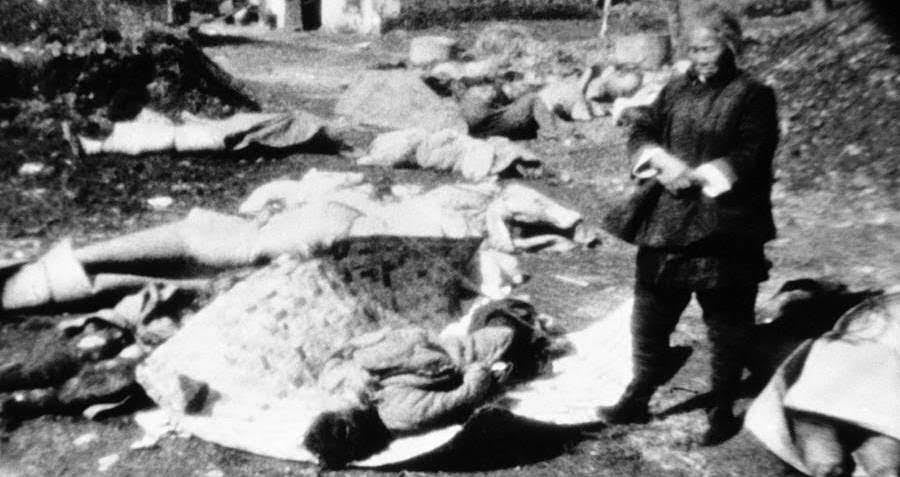

Why The Nanking Massacre Was One Of The Worst Acts Of Genocide During WW2
It's one of modern history's most horrific atrocities, and its deniers cannot explain away photos like these.
Using Primary Sources To Clarify the Nanking Incident
Last edited:
injinji
Well-Known Member
China has a long memory. If I were a betting man, I would bet they return the favor in the next 100 years. (now how do I hang around to collect on my bet?)
On December 13, 1937, the Japanese Imperial Army marched into China's capital city of Nanking and proceeded to murder 300,000 out of 600,000 civilians and soldiers in the city. The six weeks of carnage would become known as the Rape of Nanking and represented the single worst atrocity during the World War II era in either the European or Pacific theaters of war.
The actual military invasion of Nanking was preceded by a tough battle at Shanghai that began in the summer of 1937. Chinese forces there put up surprisingly stiff resistance against the Japanese Army which had expected an easy victory in China. The Japanese had even bragged they would conquer all of China in just three months. The stubborn resistance by the Chinese troops upset that timetable, with the battle dragging on through the summer into late fall. This infuriated the Japanese and whetted their appetite for the revenge that was to follow at Nanking.
After finally defeating the Chinese at Shanghai in November, 50,000 Japanese soldiers then marched on toward Nanking. Unlike the troops at Shanghai, Chinese soldiers at Nanking were poorly led and loosely organized. Although they greatly outnumbered the Japanese and had plenty of ammunition, they withered under the ferocity of the Japanese attack, then engaged in a chaotic retreat. After just four days of fighting, Japanese troops smashed into the city on December 13, 1937, with orders issued to "kill all captives."
Their first concern was to eliminate any threat from the 90,000 Chinese soldiers who surrendered. To the Japanese, surrender was an unthinkable act of cowardice and the ultimate violation of the rigid code of military honor drilled into them from childhood onward. Thus they looked upon Chinese POWs with utter contempt, viewing them as less than human, unworthy of life.
The elimination of the Chinese POWs began after they were transported by trucks to remote locations on the outskirts of Nanking. As soon as they were assembled, the savagery began, with young Japanese soldiers encouraged by their superiors to inflict maximum pain and suffering upon individual POWs as a way of toughening themselves up for future battles, and also to eradicate any civilized notions of mercy. Filmed footage and still photographs taken by the Japanese themselves document the brutality. Smiling soldiers can be seen conducting bayonet practice on live prisoners, decapitating them and displaying severed heads as souvenirs, and proudly standing among mutilated corpses. Some of the Chinese POWs were simply mowed down by machine-gun fire while others were tied-up, soaked with gasoline and burned alive.
After the destruction of the POWs, the soldiers turned their attention to the women of Nanking and an outright animalistic hunt ensued. Old women over the age of 70 as well as little girls under the age of 8 were dragged off to be sexually abused. More than 20,000 females (with some estimates as high as 80,000) were gang-raped by Japanese soldiers, then stabbed to death with bayonets or shot so they could never bear witness.
Pregnant women were not spared. In several instances, they were raped, then had their bellies slit open and the fetuses torn out. Sometimes, after storming into a house and encountering a whole family, the Japanese forced Chinese men to rape their own daughters, sons to rape their mothers, and brothers their sisters, while the rest of the family was made to watch.
Throughout the city of Nanking, random acts of murder occurred as soldiers frequently fired their rifles into panicked crowds of civilians, killing indiscriminately. Other soldiers killed shopkeepers, looted their stores, then set the buildings on fire after locking people of all ages inside. They took pleasure in the extraordinary suffering that ensued as the people desperately tried to escape the flames by climbing onto rooftops or leaping down onto the street.
The incredible carnage - citywide burnings, stabbings, drownings, strangulations, rapes, thefts, and massive property destruction - continued unabated for about six weeks, from mid-December 1937 through the beginning of February 1938. Young or old, male or female, anyone could be shot on a whim by any Japanese soldier for any reason. Corpses could be seen everywhere throughout the city. The streets of Nanking were said to literally have run red with blood.
Those who were not killed on the spot were taken to the outskirts of the city and forced to dig their own graves, large rectangular pits that would be filled with decapitated corpses resulting from killing contests the Japanese held among themselves. Other times, the Japanese forced the Chinese to bury each other alive in the dirt.
After this period of unprecedented violence, the Japanese eased off somewhat and settled in for the duration of the war. To pacify the population during the long occupation, highly addictive narcotics, including opium and heroin, were distributed by Japanese soldiers to the people of Nanking, regardless of age. An estimated 50,000 persons became addicted to heroin while many others lost themselves in the city's opium dens.
In addition, the notorious Comfort Women system was introduced which forced young Chinese women to become slave-prostitutes, existing solely for the sexual pleasure of Japanese soldiers.
News reports of the happenings in Nanking appeared in the official Japanese press and also in the West, as page-one reports in newspapers such as the New York Times. Japanese news reports reflected the militaristic mood of the country in which any victory by the Imperial Army resulting in further expansion of the Japanese empire was celebrated. Eyewitness reports by Japanese military correspondents concerning the sufferings of the people of Nanking also appeared. They reflected a mentality in which the brutal dominance of subjugated or so-called inferior peoples was considered just. Incredibly, one paper, the Japan Advertiser, actually published a running count of the heads severed by two officers involved in a decapitation contest, as if it was some kind of a sporting match.
In the United States, reports published in the New York Times, Reader's Digest and Time Magazine, were greeted with skepticism from the American public. The stories smuggled out of Nanking seemed almost too fantastic to be believed.
Overall, most Americans had only a passing knowledge or little interest in Asia. Political leaders in both America and Britain remained overwhelmingly focused on the situation in Europe where Adolf Hitler was rapidly re-arming Germany while at the same time expanding the borders of the Nazi Reich through devious political maneuvers.
Back in Nanking, however, all was not lost. An extraordinary group of about 20 Americans and Europeans remaining in the city, composed of missionaries, doctors and businessmen, took it upon themselves to establish an International Safety Zone. Using Red Cross flags, they brazenly declared a 2.5 square-mile area in the middle of the city off limits to the Japanese. On numerous occasions, they also risked their lives by personally intervening to prevent the execution of Chinese men or the rape of women and young girls.
These Westerners became the unsung heroes of Nanking, working day and night to the point of exhaustion to aid the Chinese. They also wrote down their impressions of the daily scenes they witnessed, with one describing Nanking as "hell on earth." Another wrote of the Japanese soldiers: "I did not imagine that such cruel people existed in the modern world." About 300,000 Chinese civilians took refuge inside their Safety Zone. Almost all of the people who did not make it into the Zone during the Rape of Nanking ultimately perished.

Exposing The Rape Of Nanking
THE CHRONICLE OF humankind's cruelty is a long and sorry tale. But if it is true that even in such horror tales there are degrees of ruthlessness, then few atrocities can compare in intensity and scale to the rape of Nanking during World War II.www.newsweek.com
World Perceptions on the Rape of Nanking

Why The Nanking Massacre Was One Of The Worst Acts Of Genocide During WW2
It's one of modern history's most horrific atrocities, and its deniers cannot explain away photos like these.allthatsinteresting.com
Using Primary Sources To Clarify the Nanking Incident
BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
FIFY, they like the long game as well.China has a long memory. If I were a betting man, I would bet they return the favor in the next1001000 years. (now how do I hang around to collect on my bet?)
Similar threads
- Replies
- 105
- Views
- 12K
- Replies
- 324
- Views
- 26K














