HYPHOTONFLUX
Well-Known Member

What are LEDs?
Light emitting diodes (LEDs) are a type of light source that uses solid-state semiconductor chips to produce light when an electric current flows through them. This allows them to produce more photons (light) while using less electricity than older HID technologies, such as high-pressure sodium (HPS) lights or ceramic metal-halide (CMH) lights. LED light sources have been found in commercial products for nearly half a century, but they have only recently begun to see use in indoor horticulture.
LEDs use far less energy to produce the same amount of light when compared to HPS or CMH. This can be measured using efficacy, which takes the amount of light produced by a grow light (µmol/s) and compares it to the amount of energy used (Joules/s). It is nearly 30% more efficient than the 1000W DE HPS fixture. For cultivators who have limited access the electricity, this can mean being able to have more lights at your facility without exceeding your buildings energy limits or compromising light intensity.
Produces Less Heat
Due to the energy efficiency of LEDs, grow lights using LEDs create much less heat compared to traditional light sources. HPS and CMH fixtures produce lots of heat when operating which, besides making them less efficient, creates a number of issues and limitations for indoor growers. In many places, particularly warmer climates, that excess heat needs to be removed from the grow room to maintain an optimal temperature for your grow environment. This means installing and running expensive HVAC (air conditioning) systems in your grow room. These systems use large amounts of energy to lower the temperature of your grow environment, which increases the operating cost of your grow. Because LED grow lights produce much less heat, those HVAC systems will not have to work as hard to maintain an optimal temperature for your grow room thus lowering your cost.
Can Hang Closer to Canopy
A secondary benefit of LED grow lights producing less heat is that they can be placed closer to the canopy of your plants. HPS/CMH grow lights can burn plants if placed too close to the canopy due to the large amount of heat they produce. This means you need to leave more space between them and your canopy. LED grow lights can be placed as little as a foot above the canopy which offers a number of benefits. First, it allows you to grow vertically on racks. Multi-level grow operations enable cultivators to grow more plants in less space than would traditionally be needed. In regions where space is limited or real-estate is expensive, multi-level grows can increase a cultivator’s output while reducing their expenses. Additionally, placing your grow lights closer to the canopy increases the amount of light that reaches your plants. Light is absorbed by particles in the air. So, the higher your fixture is above your canopy, the less light will end up reaching your plant. Light spillage is also an issue in some grow set-ups. Lights hung higher above the canopy spread their light over a larger area. This can lead to light being wasted as it spreads out beyond the canopy and doesn’t hit any plants. Hanging your fixtures closer to the canopy reduces this effect and focuses light on the desired areas.
What's the difference on palnts ?
Sustainably double yield – By deploying a vertical farming cultivation system, you can increased its yield per room from 100-125 pounds per harvest under HPS to 200-250 pounds per harvest under purpose-built horticulture LEDs, while only increasing power consumption by five percent.
Achieve faster cycle time – Bench turns are faster as crops mature in eight weeks, instead of nine, which will result in 35 additional days of cultivation per year.
Provide increased uniformity – When compared to HPS, the LED lights are delivering more energy to the lower portion of the plant canopy which is resulting in higher yields, with notable improvements to flower size and weight throughout the canopy.
Comparison of results
1.

2.
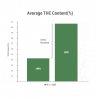
3.
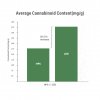
Enhance secondary metabolite profiles
Compared to HPS-grown cannabis, cannabinoid and terpene production increased 11 percent on average. New cannabinoids emerge, which were completely absent under HPS lighting.
*Data in the charts are based on the most recent harvest results


